At a time when the labor landscape is characterized by a deficit in workers and skyrocketing demand, the top brass is dealing with the question of what is an msp in staffing is and whether this specific scheme can regulate the complex contingent hiring. The compressed answer is: yes — if equipped and governed well. An MSP (Managed Service Provider) is one of the ways to centralize vendors, standardize processes and orchestrate your contingent workforce data to get rid of waste while being able to speed up, raise quality and ensure compliance.
In the very start, MSP is more than a buying desk for staffing solutions. It is a powerful operating system that can be used in an administrative manner to scale operations that include vendor management, analytics, and governance in the areas of temp staffing, contract labor, and project-based engagements. The ultimate result is durable workforce optimization which is done through hiring managers less friction, procurement, HR’s clearer controls, and better experiences for talent.
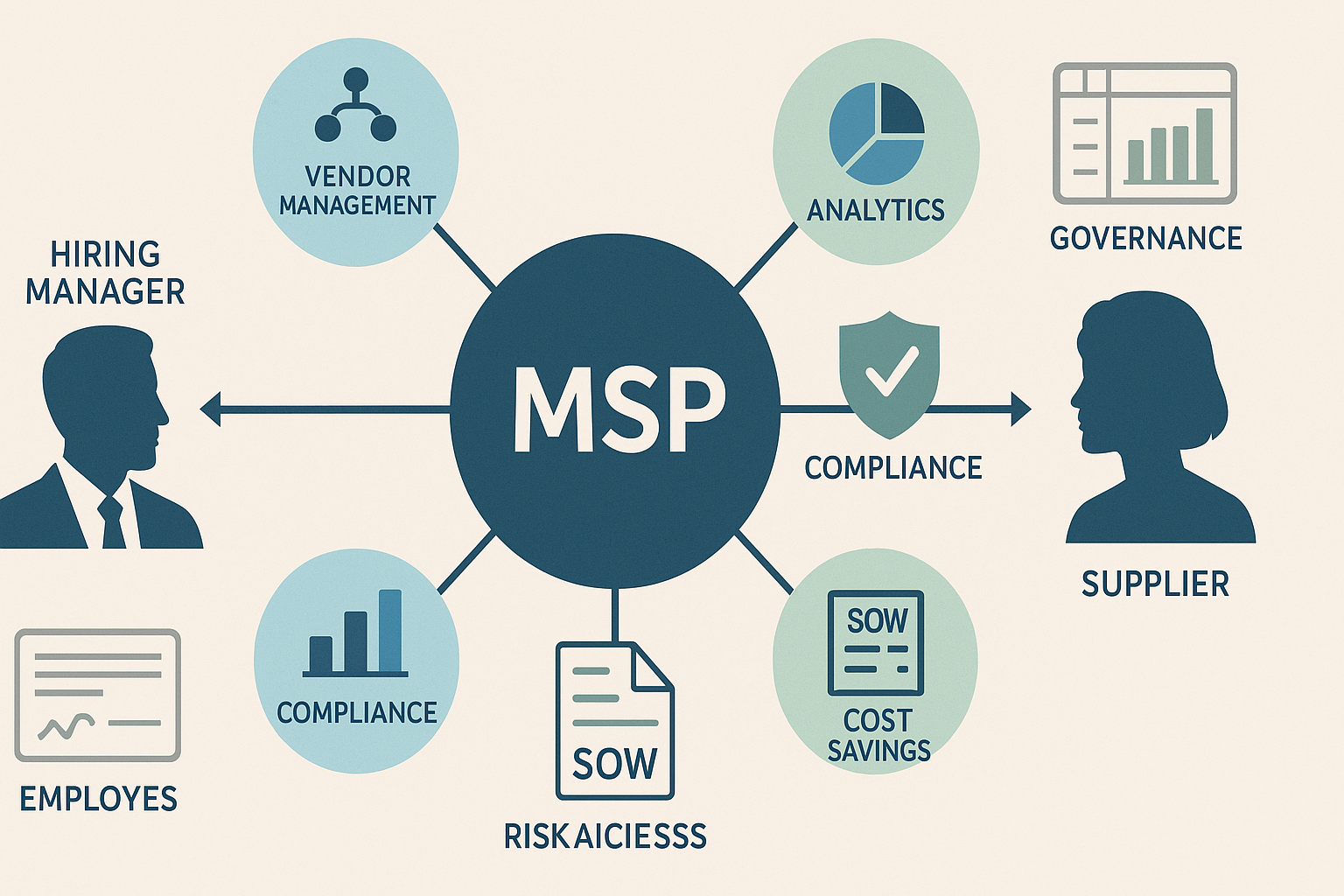
What is an MSP in Staffing?
Definition and Overview
A subcontractor public enterprise is a Managed Service Provider that in staffing is a third-party organization that alongside tracking and analyzing the labor of non-employees within a company (contractors, temps, and statement-of-work teams) also optimizes them. The MSP goes between your business and several staffing agencies that adopt a standardized service delivery model and a vendor management system (VMS) that coordinates requisitions, sourcing, onboarding, time/expense, and invoicing. It establishes a governance framework that spans the entire MSP (firewalls to master service agreement and program playbooks) starting from the price rules, rate negotiation, performance standards, data security, and compliance.
The MSP gets to the point that it assumes command over your workforce which is temporary. It integrates workforce management, talent management,talent acquisition and recruitment outsourcing, integrates with Finance and Procurement departments, and allows vendor neutral sourcing when needed. SOW projects feature the MSP coordinating SOW management, milestone-based payments, and delivery validation as part of your larger outsourcing portfolio.
Brief Overview of What is MSP & VMS in Recruiting Industry | US Staffing
Key Functions of an MSP
- Vendor performance management and supplier consolidation to simplify the supplier base while preserving niche expertise.
- Centralized rate negotiation, rate-card governance, and pricing guidance to drive measurable cost savings and transparency in cost to hire.
- Program-level workforce analytics, performance metrics, and dashboards to improve workforce efficiency and decision-making.
- Demand forecasting and workforce planning support, enabling proactive talent pipelines and capacity modeling.
- Compliance analytics, audit readiness, and risk mitigation through background check standards, supplier risk assessment, and policy enforcement.
- Onboarding efficiency, payroll integration, and digital credentialing to accelerate start dates and reduce manual touchpoints.
- Contractor management, talent pooling, diversity sourcing, redeployment strategy, and workforce segmentation to improve fill rates and retention.
- Program MSP governance, SLAs, and issue escalation embedded in your procurement integration and enterprise controls.

Advantages of Implementing an MSP
Cost Savings and Efficiency
An MSP threatens fragmented spend by creating a single staffing model with accountable controls. Standardized rate cards, supplier tiers, and automated approvals will give you the direct benefit of staff optimization. Processes are more streamlined, which leads to a reduction in cycle time and administrative overhead, resulting in direct cost savings and a decrease in the fully loaded cost to hire. Armed with the clear service delivery model roles (business, MSP, and suppliers), rework is minimized, and operational workforce bloats get unlocked.
Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management
In the context of various jurisdictions and fast-evolving regulations, compliance can’t be discretionary. The MSP by enforcing uniform onboarding and verification, providing constant compliance analytics, and keeping audit-organization-readiness artifacts. Program tools are dedicated to supplier risk assessment, privacy, and data security controls as well as cross-border policy alignment that is backstopped with a documented governance framework and enterprise risk mitigation practices.
Improved Access to Talent
MSPs manage to grow the labor pool through a mix of different workforce solutions: an outsourcing partner for recruitment in hard-to-fill roles, niche staffing agencies for specialized skill sets, and curated talent pools for recurrent needs. The program lies in bridging the gap between hiring speed and the acquisition of quality resources through real-time analytical workforce data, strategic recruitment, smart vendor neutral sourcing to reduce time-to-submit or time-to-start.
How to Implement an MSP in Your Organization
Assessing Your Workforce Needs
Begin with diagnostics of your non-employee labor: labor spend by category, suppliers, locations, and risk profile. Identify bottlenecks, duplicate vendors, and inconsistent pricing as your baseline for MSP implementation goals. Link results with business revenues: fill-rate targets, cycle-time SLAs, compliance risk reduction, and manager NPS. Cover macro workforce trends, high seasons and broader staffing challenges to size the project and inform staffing strategy.
Selecting the Right MSP Provider
During the process, you should list out possible candidates based on their fluency in the business, geographic coverage, and overall reliability of the technology (VMS features, analytics, integrations). Determine the msp governance method they follow and what to do in the event of escalations or changes. Request examples of procurement integration, sow management, and master service agreements that align with your risk posture.Therefore if neutrality is very important, the supplier must abide by vendor neutral sourcing with an open rule on supplier engagement and vendor performance management.
Integrating MSP with Existing Processes
Transition planning is essential.Based on details, specify transition pathways which will map requisition flows, approval hierarchies, and reporting lines. Integrate the VMS with HCM/ERP for payroll integration, cost-center validation, and single-sign-on. Standardize intake with role templates and skills taxonomies so as to speed up sourcing and improve match quality. Codify onboarding efficiency steps, define performance metrics and align recruitment process handoffs so the MSP complements — not disrupts — your current HR outsourcing or internal TA operations.

Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Managing Vendor Relationships
Suppliers may get the impression of being overlooked or margin loss. Overcome this by putting the clear tiering rules on the open, vendor performance management scorecards on the sponsoring, and predictable distribution logic on the paying side. Use supplier consolidation where fragmentation hurts performance, but preserve specialty partners for scarce skills. Encourage collaboration with calibrated feedback, quarterly business reviews, and fair dispute resolution — especially in a vendor neutral sourcing model.
Ensuring Compliance Across Multiple Jurisdictions
Each state and country has different rules on background checks, taxes, co-employment, and IP. Build your governance framework with global guardrails and then localize them in the VMS via country-specific workflows, compliance analytics, and documentation libraries for audit readiness. Incorporate supplier risk assessment and privacy data security checks in the onboarding process to lessen the exposure.
Maintaining Flexibility and Scalability
Business cycles change. Contingent labor arrangement should have elasticity by the tiered supplier pools, curated talent pooling and a formal redeployment strategy to retain the best talents between assignments.Your contingent labor program should be architected for elasticity so you can scale without degrading service. Combine demand forecasting with a scenario plan that enables you to scale up or down quickly while offering quality service. Similarly MSP should be the one to alert you on market shifts and rate negotiation prompts to keep the program competitive across the whole staffing industry.
Future Trends in MSP Staffing
Technological Advancements
Expect embedded automation and intelligence throughout the full stack of processes with AI-assisted matching, active rate benchmarking, and predictive workforce analytics being the drivers for better sourcing and workforce segmentation in real-time. Compliance as a technology will merge more with the VMS, increasing compliance analytics, incorporating identity verification, and ensuring constant audit readiness. The use of APIs will embrace the utilization of procurement integration and will enhance the model for service delivery orchestration.
Evolving Workforce Dynamics
The mixture of full-time employees, temporary staffing, and contract labor will go on changing toward a skill-based engagement. Global talent markets will, at one side, demand diversity goals to fasten diversity sourcing, and at the other side, seek localized policy playbooks to cater to smarter contractor management. So what is an msp in staffing doing about it? Companies will keep inquiring about the role of msp in staffing partnerships in managing risk and brand experience in a borderless contingent workforce.
Strategic Workforce Planning
More and more executives are now positioning MSPs as tools for achieving profound staffing optimization and reshaping workforce planning.The programs will dual supplier SLAs with business KPIS, link sop deliverables to milestone based payments, and refine the category-specific recruitment strategy. As pressure from the board rises, the leaders will once again explain what besides lowering the cost is an msp in staffing worth — such as resilience, visibility, and risk mitigation aligned with multi-year portfolios.
Ending
In case you have battled with erratic suppliers, broken pricing, and compliance issues, an MSP is a proven way to gain control and clarity. It is through central vendor management, codified msp governance rules and putting decisions on the workforce analytics that the model can get quality, speed, and risk posture strengthened all at once. Your assessment of providers should readdress the main question — what is an msp in staffing for your business? An answer should be a transparent, agile, and value measurable by data and protected by governance leap that reflects the realities of today’s workforce dynamics.

No Responses